Research Highlights
Professor Xianran Xing’s team has proposed a new interphase approach for the adjustment of the lattice strain through material lattice strain engineering, that is, the formation of a mutual strain regulation by growing two materials with a similar crystal structure but different lattice parameters in a single epitaxial film, as shown in Fig. 1. The lattice strain can introduce significant changes to the physical and chemical properties of the material, the effects of which can be widely applied to the fields of superconductivity, giant magnetoresistance, multiferroics, and catalysis. The team has realized this concept by growing a ferroelectric material, PbTiO3, and a non-ferroelectric material, PbO, which have different lattice parameters, into a coherently matched epitaxial film on the SrTiO3 substrate. This approach has increased the lattice distortion of PbTiO3 to c/a = 1.238 while leaving the bulk at 1.065. In addition, the material achieves an unprecedented giant remanent polarization of 236.3 μC/cm2, which is twice the highest value of the currently known ferroelectrics, while enhancing the stable temperature of the ferroelectrics phase from 490 ℃ to 725 ℃. The relevant results were published in Science [361(6401):494-497] on August 3, 2018 (Fig. 4).
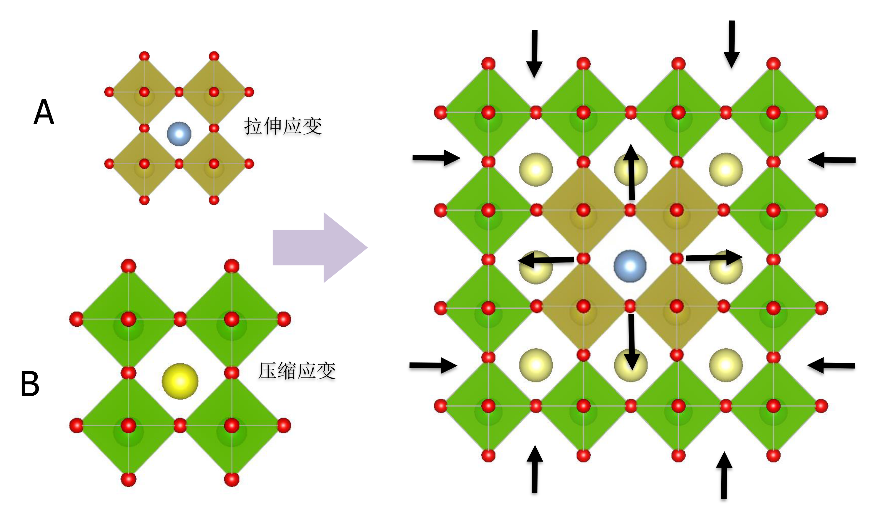
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of “interphase strain” lattice control
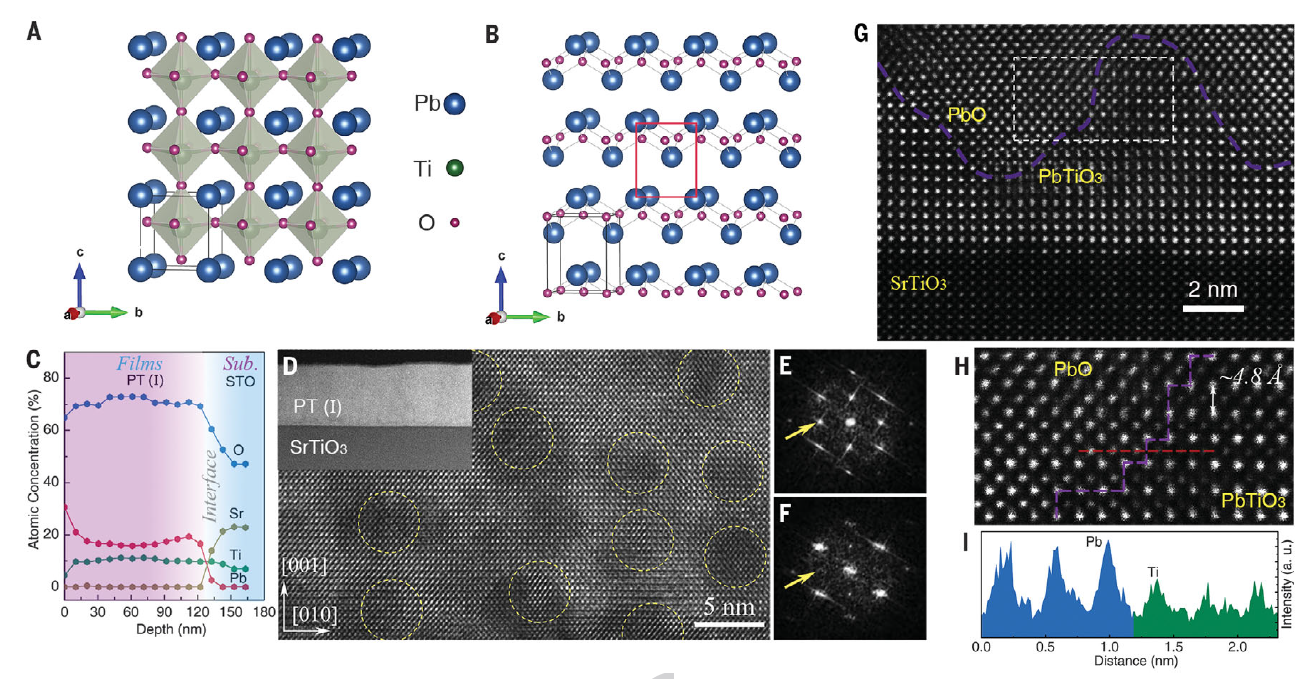
Fig. 2 Microstructure and giant ferroelectric polarization gene of the PbTiO3/PbO epitaxial film
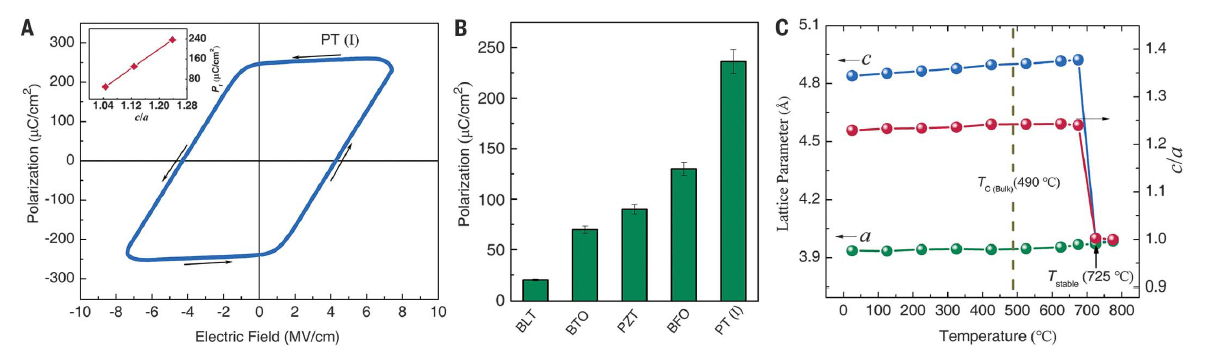
Fig. 3 Giant ferroelectric polarization and temperature stability


Fig. 4 Article page